
11:45am Friday, June 21 to Monday, September 23
The June solstice 2019—the summer solstice in the Northern Hemisphere—will occur on June 21. Here’s what you need to know about the longest day of the year—plus more fun facts about the first day of summer.
WHEN IS THE SUMMER SOLSTICE?
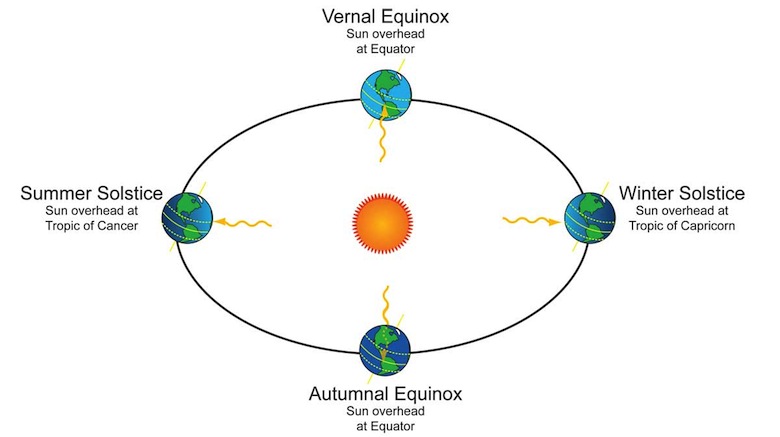
In 2019, the June solstice is Friday, June 21, at 11:54 A.M. EDT. This date marks the official beginning of summer in the Northern Hemisphere, occurring when Earth arrives at the point in its orbit where the North Pole is at its maximum tilt (about 23.5 degrees) toward the Sun, causing the longest day and shortest night of the calendar year. By longest “day,” we mean the longest period of sunlight. At the June solstice, the Northern Hemisphere receives sunlight at the most direct angle for the year.
| Year | Summer Solstice (Northern Hemisphere) |
| 2019 | Friday, June 21 |
| 2020 | Saturday, June 20 |
| 2021 | Sunday, June 20 |
| 2022 | Tuesday, June 21 |
WHAT IS THE SUMMER SOLSTICE?
In the Northern Hemisphere, the June solstice (aka summer solstice) occurs when the Sun reaches both its highest and northernmost points in the sky. It marks the start of summer in the northern half of the globe. (In contrast, the June solstice in the Southern Hemisphere is when the Sun is at its lowest point in the sky, marking the start of winter.)
The word “solstice” comes from Latin solstitium—from sol (Sun) and stitium (still or stopped), reflecting the fact that on the solstice, the Sun appears to stop “moving” in the sky as it reaches its northern- or southernmost point (declination) for the year, as seen from Earth. After the solstice, the Sun appears to reverse course and head back in the opposite direction. The motion referred to here is the apparent path of the Sun when one views its position in the sky at the same time each day, for example at local noon. Over the year, its path forms a sort of flattened figure eight, called an analemma. Of course, the Sun itself is not moving (unless you consider its own orbit around the Milky Way galaxy); instead, this change in position in the sky that we on Earth notice is caused by the tilt of Earth’s axis as it orbits the Sun, as well as Earth’s elliptical, rather than circular, orbit.
The timing of the June solstice is not based on a specific calendar date or time; it all depends on when the Sun reaches its northernmost point from the equator. Therefore, the solstice won’t always occur on the same day. Currently, it shifts between June 20, 21, and 22.
The Summer Solstice is the day with the longest period of sunlight. Notice how the Sun appears highest in the sky at the solstice; its rays strike Earth at a more direct angle, causing the efficient warming we call summer. Because the Sun is highest in the sky on this day, you’ll notice that your shadow (at local, or solar, noon, not clock-time noon) is the shortest that it will be all year. [Local noon is when the Sun crosses the local meridian (an imaginary line between the North and South poles) and is highest in the sky for the day.]
For those who live in the Southern Hemisphere, this is the shortest day of the year and marks the arrival of winter.
 Road Rage Incident results in Felony OWI Arrest
Road Rage Incident results in Felony OWI Arrest
 Governor Braun Launches Office to Support Main Street Small Business
Governor Braun Launches Office to Support Main Street Small Business
 JD Shelburne to Debut at the Grand Ole Opry
JD Shelburne to Debut at the Grand Ole Opry






